Steel foil is an incredibly versatile material that finds a multitude of applications in our daily lives. From electronic components to food packaging, it’s a staple in numerous industries. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the world of steel foil, exploring its many variations including the steel foil sheet, carbon steel foil, stainless steel sheet, and even related materials like titanium foil and magnetic foil. Discover the unique properties that each type offers, learn about their manufacturing processes, and uncover how they contribute to various sectors including healthcare, aerospace, and construction. This exploration will help you understand why steel foil is such a vital material in the modern world. The journey awaits, let’s unravel the many layers of steel foil together!
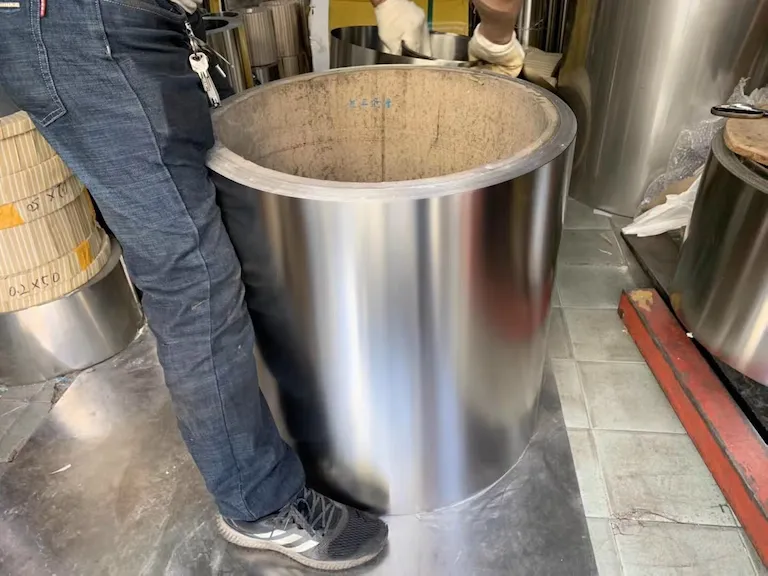

Steel foil, a very thin sheet of steel, has diverse applications in numerous industries due to its beneficial properties. Its main characteristics are its exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to various environmental factors. The composition of steel lends it a unique property of magnetism, making it a versatile material.
Steel foil is made through a process called rolling, where steel is pressed between heavy rolls until it reaches the desired thinness. This manufacturing process is highly controlled to ensure the steel foil’s thickness and quality meet the industry standards.
One of the popular types of steel foil is the stainless steel foil, often used in food processing and medical industries due to its anti-corrosive properties. Another variant is the mild steel foil, offering less carbon content than its counterparts, making it easier to shape and weld.
The third variant is the carbon steel foil, distinguished by its high carbon content, providing it increased strength and hardness. All these types of steel foils have a magnetic property which extends their usability across different industries.
A rather exotic type of foil used in special applications is titanium foil. While not a type of steel, titanium foil shares some applications with steel foil due to its high strength and corrosion resistance.
The properties of steel foil vary depending on its composition, which can be adjusted to meet specific application needs. Typically, steel foil exhibits excellent strength and hardness. Despite its thin structure, it maintains rigidity and resistance against deformation.
The durability of steel foil is another notable property. With proper care and use, it can retain its quality for a long period, making it cost-effective for many businesses. Additionally, steel foil demonstrates significant resistance against various environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, and corrosive elements.
The magnetic nature of steel foil is an inherent property of its iron content. This makes steel foil an attractive choice for applications where magnetism plays a vital role, like in electrical and electronic industries.
A unique property seen in certain types of steel foil, like stainless steel, is its corrosion resistance. Due to the presence of chromium, it forms a passive film on the surface that prevents corrosion, making it ideal for food handling and medical applications.
Steel foil, thanks to its unique properties, is widely used in various industries. In the food industry, the stainless steel foil acts as an excellent packaging material due to its resistance to corrosion and ability to maintain food quality.
In the electronics industry, steel foil’s magnetic property is leveraged for components like inductors and transformers. Additionally, the durability and heat resistance of steel foil make it an optimal choice for heat shields and insulation in electrical systems.
Industrial applications of steel foil are numerous. It’s used in the construction of machinery parts, and due to its excellent formability, it’s also used in fabrication of various structures. Carbon steel foil, given its high strength and hardness, is often used in tools and blades.
Healthcare is another sector that benefits from steel foil. Stainless steel, for its anti-corrosive nature and sterilizability, is used in medical equipment and implants.
Lastly, an emerging use of steel foil is in renewable energy sector, specifically in hydrogen fuel cells. Here, stainless steel foil acts as an interconnector due to its high electrical conductivity and stability under operational conditions.
Steel, an iron alloy, possesses inherent magnetic properties due to the presence of iron. Steel foil, therefore, is indeed magnetic. This property is critical for several applications, especially in the electronics industry where it is used in components such as transformers and inductors.
However, not all types of steel foil maintain this magnetic property. For instance, certain types of stainless steel foils, such as those of the austenitic grade, are not magnetic. The reason lies in their microstructure – the nickel content in austenitic stainless steel alters the iron’s magnetic arrangement, rendering it non-magnetic.
On the other hand, ferritic and martensitic grades of stainless steel foils retain their magnetic properties. This is due to their iron-rich composition and microstructural arrangement.
The production of steel foil involves several steps. It starts with the extraction of iron from iron ore in a blast furnace. The extracted iron is mixed with carbon and other elements to create steel.
Once steel is formed, it’s time to make it into a foil. This is achieved through a process called rolling. Rolling involves passing the steel through heavy rolls, applying significant pressure to flatten and thin out the steel.
The rolling process has two stages: hot rolling and cold rolling. Hot rolling is the initial step, where the steel is heated above its recrystallization temperature and then rolled. This process breaks down the steel’s old microstructure and forms a new one, enhancing the steel’s mechanical properties.
After hot rolling, the steel undergoes cold rolling. This is done at room temperature and gives the steel a smoother surface finish and precise dimensions. The steel is rolled until it reaches the thinness of a foil.
Post rolling, steel foils may undergo further processes like annealing, where it’s heated and cooled under controlled conditions to relieve stresses and increase ductility. The steel foil may also be coated or treated to enhance specific properties based on its intended application.
Mild steel foil is a type of steel foil made from a low carbon steel alloy, commonly referred to as mild steel. This type of steel contains less carbon than other steel types, typically around 0.05-0.25% by weight.
Because of its low carbon content, mild steel foil is more ductile, malleable, and easier to weld than higher carbon steel types. This makes it an excellent choice for applications requiring shaping, bending, or welding.
Mild steel foil is often used in automobile body manufacturing, domestic appliances, and construction. Its excellent machinability and weldability make it a versatile choice for these and many other applications.
Despite its many advantages, mild steel foil has a significant drawback – it’s not as resistant to corrosion as its stainless steel counterpart. Therefore, it often requires a protective coating or treatment to improve its resistance to environmental factors.
Carbon steel foil is a type of steel foil made from carbon steel, which is distinguished by its higher carbon content compared to other types of steel. The carbon content in carbon steel typically ranges from 0.12% to 2.0%.
The high carbon content significantly enhances the hardness and strength of the steel, making carbon steel foil a suitable choice for applications requiring durability and resistance to wear. This makes it a popular material for tools, blades, and heavy machinery components.
However, the increased carbon content also makes carbon steel foil less ductile and more difficult to weld than milder steel types. This requires the use of specialized welding techniques when working with carbon steel.
Carbon steel is also prone to corrosion, much like mild steel. Therefore, carbon steel foil often requires a protective coating or additional treatments to resist rusting and other forms of corrosion.
The primary difference between steel foil and stainless steel sheet lies in their thickness and composition. Steel foil is much thinner than a sheet and can be as thin as 0.01mm, whereas a stainless steel sheet is generally thicker, typically starting from around 0.5mm
.
Compositionally, stainless steel is distinguished by the addition of at least 10.5% chromium, which imparts significant anti-corrosive properties. This makes stainless steel sheet a preferred choice in applications where resistance to corrosion is critical, such as in kitchen appliances, medical equipment, and food processing machinery.
On the other hand, steel foil, while it can be made from various types of steel, including stainless steel, is valued for its thinness and flexibility. Its applications are more diverse, ranging from electronic components to food packaging, and can be selected based on the specific type of steel used.
It’s important to note that stainless steel sheet can also be produced in foil thicknesses, merging the benefits of stainless steel’s corrosion resistance with the versatility of foil.
Titanium foil is a type of metallic foil made from titanium, a strong, light, and corrosion-resistant metal. While titanium isn’t a type of steel, it shares some properties and applications with steel foil, which often leads to comparisons between the two.
Like steel foil, titanium foil is made through a process of rolling where titanium is pressed until it achieves a thin, foil-like thickness. This process yields a foil that is not only light and strong but also highly resistant to corrosion and temperature variations.
Titanium foil is used extensively in aerospace applications due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and its ability to withstand extreme temperatures. It’s also used in medical applications because it’s bio-compatible, meaning it can be safely used for medical implants without causing harmful reactions in the body.
While titanium foil possesses several superior properties, it comes with a higher cost compared to steel foil. Therefore, its use is generally reserved for applications where its specific advantages can justify the cost.
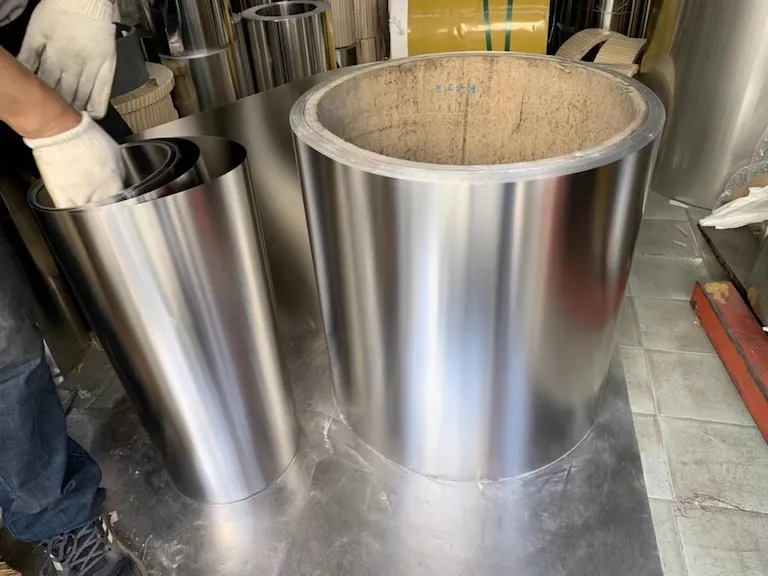

A stainless steel roll refers to a roll of stainless steel foil or sheet, which can be unwound and cut into different sizes based on the needs of the user. It comes in various thicknesses, widths, and grades, offering options for different applications.
The primary benefit of a stainless steel roll lies in its ease of storage and distribution. The rolled format allows for efficient use of space and ease of transportation. Furthermore, the ability to cut the roll to specific sizes as needed reduces waste and provides flexibility for varied uses.
Stainless steel rolls are commonly used in sectors such as construction, automotive, food service, and healthcare, among others. The anti-corrosive properties of stainless steel make these rolls suitable for environments exposed to moisture and other corrosive elements.
Moreover, stainless steel rolls find their use in manufacturing processes where large quantities of material are needed, such as in the production of kitchen appliances, medical instruments, and automobile parts.
Magnetic foil is a type of foil that has magnetic properties. The term "magnetic foil" often refers to foils made from magnetic materials, such as iron or certain types of steel, including some forms of stainless steel.
Due to their magnetic properties, these foils are used in various applications where magnetism is required. This includes use in electrical transformers and inductors, magnetic shielding, magnetic sensors, and in some types of data storage.
Steel foil, given its inherent magnetic properties due to its iron content, can be classified as a type of magnetic foil. However, as mentioned earlier, not all steel foils are magnetic. Certain grades of stainless steel, like the austenitic grade, are not magnetic due to their nickel content.
On the other hand, ferritic and martensitic stainless steel, as well as mild steel and carbon steel foils, are all magnetic, and therefore can be referred to as magnetic foils.
In conclusion, the world of steel foil is a fascinating one, with its many types, properties, and uses. Whether it's the commonplace steel foil used in food packaging, the specialized stainless steel sheet used in high-end appliances, or the high-tech magnetic foils used in electronic components, steel foil's versatility and performance make it a critical material in numerous industries. Understanding the nuances of steel foil helps in selecting the right type for a given application, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
This marks the end of the article on steel foil.

When it comes to steel foils, there are several types and thicknesses available in the market. In this article, we will focus on two main types: 304 and 316 stainless steel foils.
The 304 stainless steel foil is a popular choice due to its resistance to corrosion and oxidation. It is available in different thicknesses, with the price varying accordingly.
For a thickness of 0.002″, the price is as follows:
The 316 stainless steel foil is known for its superior corrosion resistance, especially against chlorides and chlorinated solutions. This makes it ideal for use in marine environments. The prices for different thicknesses are:
Please note that these prices are subject to change and may vary depending on the supplier and location. It is recommended to check the websites or contact the suppliers directly for the most up-to-date pricing information.
In conclusion, the cost of steel foil depends on the type, thickness, and specific requirements of your project. Always ensure to check with multiple suppliers to get the best deal.
For more information, refer to the flowchart and bar chart below:
And the table summarizing the prices:
| Steel Foil Type | Thickness | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 304 Stainless Steel Foil | 0.002″ | $50 per pound (36″ x 200′ roll), $437.71 each in a package of 2 (24″ x 50′ roll) |
| 316 Stainless Steel Foil | 0.005″ | Check website for prices (24″ x 1200″ sheet) |
| 316 Stainless Steel Foil | 0.01″ | $20 to $35 per kilogram (30mm wide roll up to 2mm thickness) |
Stay tuned for more updates on the prices of different materials in the market.
Surgical Instruments: 0.05mm stainless steel foil is used in the manufacturing of surgical instruments such as scalpels, forceps, and scissors. The material’s high strength, durability, and corrosion resistance make it ideal for these applications.
Corrosion Resistance: 0.05mm stainless steel foil has excellent corrosion resistance properties, which is essential for medical equipment manufacturing. This ensures that the equipment remains sterile and free from contamination.
Biocompatibility: The material is biocompatible, meaning it can be used in contact with human tissue without causing adverse reactions.
Durability: Stainless steel foil sheets are highly durable and can withstand harsh environments and frequent sterilization.
Conductivity: The material has excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for use in diagnostic equipment.
0.05mm stainless steel foil is an excellent material for medical equipment manufacturing. Its high strength, corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, and electrical conductivity make it ideal for a wide range of medical applications. Medical equipment manufacturers can benefit greatly from using this material to produce high-quality medical devices and instruments.
In today’s digital age, electronic devices are ubiquitous, and with the increase in electronic devices, electromagnetic interference (EMI) has become a significant concern. EMI can cause malfunctions and even damage to electronic equipment, making shielding crucial for electronic devices. 0.05mm stainless steel foil is an excellent material for electronic shielding due to its unique properties.
High Conductivity: 0.05mm stainless steel foil has excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for use in electronic shielding applications.
Corrosion Resistance: The material is highly resistant to corrosion, which is essential for electronic devices that are exposed to harsh environments.
Ductility: Stainless steel foil sheets are highly ductile and can be easily shaped and formed to fit the required shielding shape.
Strength: The material is highly resistant to impact and mechanical stress, making it an ideal choice for electronic shielding.
Circuit Board Shielding: Circuit boards contain sensitive electronic components that are prone to electromagnetic interference. Stainless steel foil sheets are used to create shields that prevent EMI from interfering with the circuit board’s function.
Cable Shielding: Cables that connect electronic devices are also prone to electromagnetic interference. Shielding these cables with 0.05mm stainless steel foil prevents EMI from interfering with the signal.
Electronic Enclosures: Electronic enclosures house electronic devices and are also prone to EMI. Using stainless steel foil sheets to shield these enclosures prevents EMI from entering the enclosure and interfering with the device.
High Efficiency: Stainless steel foil sheets are highly efficient at shielding electronic devices from electromagnetic interference.
Durability: The material is highly durable and can withstand harsh environments and frequent use.
Cost-Effective: Stainless steel foil sheets are cost-effective compared to other shielding materials, making them an ideal choice for electronic device manufacturers.
0.05mm stainless steel foil is the perfect material for electronic shielding due to its unique properties. Its high conductivity, corrosion resistance, ductility, and strength make it an excellent choice for a wide range of electronic shielding applications. Electronic device manufacturers can benefit greatly from using this material to produce high-quality electronic devices that are free from electromagnetic interference.
The aerospace industry has always been at the forefront of technological advancements. The need for lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant materials is essential to the success of the industry. 0.05mm 304 stainless steel foil has been a game-changer for the aerospace industry due to its unique properties and versatility.
Corrosion Resistance: 0.05mm 304 stainless steel foil is highly resistant to corrosion, making it an ideal material for use in harsh environments.
High Strength: The material is strong and can withstand high stresses, making it ideal for use in aircraft parts that require strength and durability.
Lightweight: 0.05mm 304 stainless steel foil is lightweight compared to other materials, making it ideal for use in aircraft and spacecraft where weight is a crucial factor.
Ductility: The material is ductile and can be easily formed and shaped to fit specific design requirements.
Aircraft Parts: 0.05mm 304 stainless steel foil is used in the manufacture of various aircraft parts, including fuel tanks, exhaust systems, and engine components.
Spacecraft Parts: The material is also used in the manufacture of spacecraft parts, including satellite components, rocket nozzles, and fuel tanks.
Heat Exchangers: 0.05mm 304 stainless steel foil is used in the manufacture of heat exchangers used in aircraft and spacecraft cooling systems.
Improved Fuel Efficiency: The lightweight properties of the material improve the fuel efficiency of aircraft and spacecraft, reducing operating costs and increasing the range of the vehicle.
Corrosion Resistance: The material’s corrosion-resistant properties ensure the longevity and durability of aircraft and spacecraft parts, reducing maintenance costs.
High Strength: The material’s high strength ensures the safety and reliability of aircraft and spacecraft, reducing the risk of mechanical failure.
Design Flexibility: The material’s ductility allows for the creation of complex and innovative designs that improve the performance and functionality of aircraft and spacecraft.
While 316 stainless steel foil is also commonly used in the aerospace industry, it is heavier and less ductile than 0.05mm 304 stainless steel foil. 316 stainless steel foil is more resistant to corrosion than 304 stainless steel foil but is also more expensive. In contrast, 0.05mm 304 stainless steel foil provides a cost-effective solution without compromising on performance.
0.05mm 304 stainless steel foil has revolutionized the aerospace industry due to its unique properties and versatility. Its lightweight, high strength, and corrosion-resistant properties make it an ideal material for use in aircraft and spacecraft parts, improving fuel efficiency, reducing maintenance costs, and ensuring the safety and reliability of the vehicle. Its design flexibility and cost-effectiveness make it a game-changer for the industry, providing a competitive edge in the market.
Here, we will provide tips on how to choose the right 0.03mm 304 stainless steel foil for your specific application. We will discuss factors such as the desired thickness, surface finish, and corrosion resistance.
In this section, we will discuss the future of 0.03mm 304 stainless steel foil and its potential applications. We will explore how advancements in technology and manufacturing processes could enhance its properties and lead to new uses.
This section will discuss the different applications of 0.03mm 304 stainless steel foil in various industries, including medical, automotive, and aerospace. We will highlight how this material is used in each industry and its specific benefits.
In this section, we will describe the manufacturing process of 0.03mm 304 stainless steel foil. We will discuss the different methods used to produce this material and how it is processed to achieve its unique properties.