People often hear about cold rolling and hot rolling. But what is hot rolled? What is cold rolled? What is the difference between the two?
The guide will describe the difference between hot rolling and cold rolling in detail.
For example, some common cold rolled steel grades include C1008, which has excellent surface finish and formability properties, and C1010, known for its high strength and machinability. Other grades like C1045 and C1075 are known for their hardness and are often used in applications like springs and cutting tools.

AISI 304; AISI 301; AISI 316;AISI 316L…
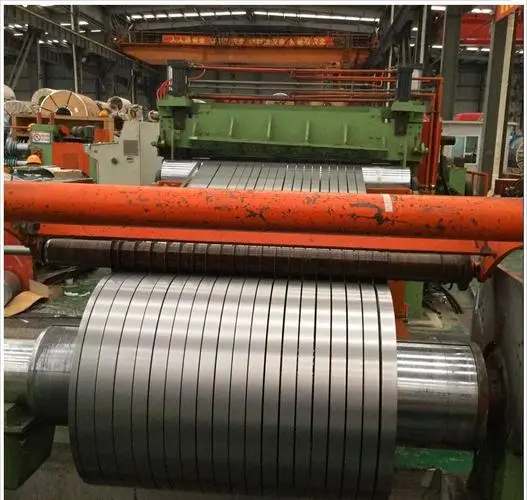
Cold rolled: Hot-rolled steel coil is used as raw material, after pickling to remove oxide scale, cold rolling is carried out. The finished product is the hard-rolled coil. The cold-work hardening caused by continuous cold deformation increases the strength, hardness, and toughness of the hard-rolled coil. The plastic index drops, so the stamping performance will deteriorate, and it can only be used for simple deformed parts. Hard-rolled coils can be used as raw materials for hot-dip galvanizing plants because hot-dip galvanizing lines are equipped with annealing lines. The weight of the rolled hard coil is generally 6 to 13.5 tons, and the steel coil is continuously rolled on the hot-rolled pickled coil at room temperature. The inner diameter is 610mm.
Cold rolling: It is processed and rolled based on a hot-rolled stainless steel plate and coil. Generally speaking, it is a process of hot rolling→pickling→cold rolling. Although rolling will also heat the steel plate during the processing process, it is still called cold rolling. Because the hot rolling is cold rolled after continuous cold deformation, the mechanical properties are relatively poor and the hardness is too high. It must be annealed to restore its mechanical properties, and those without annealing are called rolled hard coils. Rolled hard coils are generally used to make products that do not need to be bent or stretched.
Stainless Steel Chemical Composition – YAOYI Stainless Steel
Keep reading: A Complete Guide to Stainless Steel AISI 4140
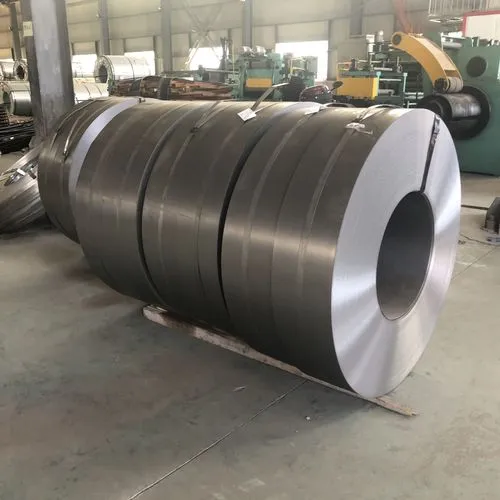

Hot rolled uses slabs (mainly continuous casting slabs) as raw materials. After heating, the rough rolling mill and the finishing mill are used to make strip steel. The hot steel strip from the last rolling mill of finishing rolling is cooled to the set temperature by laminar flow and then coiled into steel coil by the coiler. The cooled steel coil will undergo different finishing operations according to the different needs of users. Lines (flattening, straightening, cross-cutting or slitting, inspection, weighing, packaging and marking, etc.) are processed into steel plates, flat coils, and slit steel strip products. To put it simply, a piece of steel billet is heated (that is, the hot steel block that is burning red on the TV) after a few passes, and then trimmed to be straightened into a steel plate. This is called hot rolling.
Hot rolling: It is relative to cold rolling. Cold rolling is rolling below the recrystallization temperature, while hot rolling is rolling above the recrystallization temperature.
Read on:AISI 430 Stainless Steel
Try for free AISI 4140 Low Alloy Steel
These sections are primarily used in construction and engineering projects for building structures, bridges, ships, and so on.
Because it’s processed at high temperatures, it’s easier to shape and form, making it ideal for producing larger components.
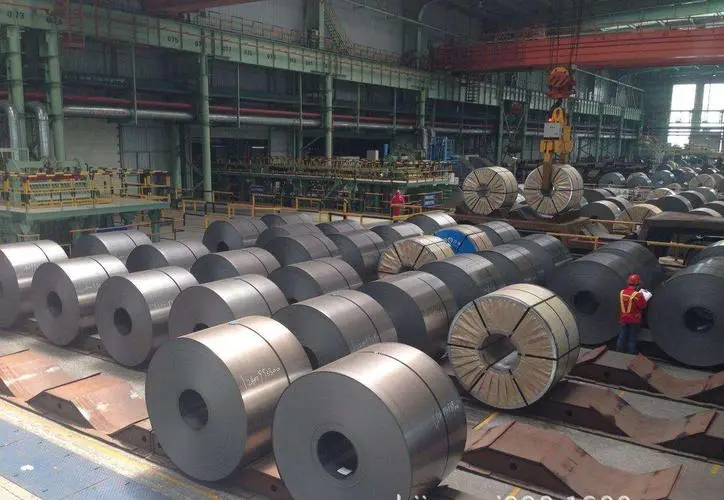

The difference between hot rolled sheet and cold rolled sheet can be attributed to the following points:
Get it now:A complete guide to AISI 410 Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance, which makes it ideal for applications exposed to harsh environments, such as kitchen appliances, medical instruments, and chemical processing equipment.
Hence, it is often preferred for applications where precision is crucial, such as automotive parts or machinery components.

Cold rolled steel sheets are used in a variety of applications that demand a high level of precision and superior surface finish. These applications range from automotive panels to appliances, furniture, and even certain types of roofing. The sheets are often coated or painted to further enhance their durability and aesthetics.
Cold rolled steel and stainless steel are suited to different applications due to their distinct properties. Cold rolled steel, with its smooth finish and dimensional accuracy, is commonly used in applications that require precision, such as machinery components and automotive parts. Stainless steel, known for its corrosion resistance, is often used in applications exposed to harsh environments, such as kitchen appliances, medical instruments, and chemical processing equipment.

Both hot rolled and cold rolled steel can be welded. However, because hot rolled steel has a scale on its surface from the hot rolling process, it may require additional preparation, such as grinding or blasting, before welding to ensure a strong weld. On the other hand, cold rolled steel often has a cleaner surface which may be easier to weld without additional preparation. Still, the choice between the two will depend on the specific application, and both may require preheating or other welding procedures based on the composition and thickness of the material.

Cold rolled steel grades are determined by factors like chemical composition and mechanical properties. For example, some common cold rolled steel grades include C1008, which has excellent surface finish and formability properties, and C1010, known for its high strength and machinability. Other grades like C1045 and C1075 are known for their hardness and are often used in applications like springs and cutting tools.
