316L stainless steel is a low-carbon version of 316 stainless steel, an austenitic stainless steel alloy known for its excellent corrosion resistance and strength. the “L” in 316L indicates a lower carbon content, which improves its weldability and reduces the risk of carbide precipitation during welding. Some key 316L stainless steel properties include: corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, low temperature resistance, weldability, mechanical properties and formability. We will tell you more about them.
Learn more about the Everything you need to know about SUS SS304.
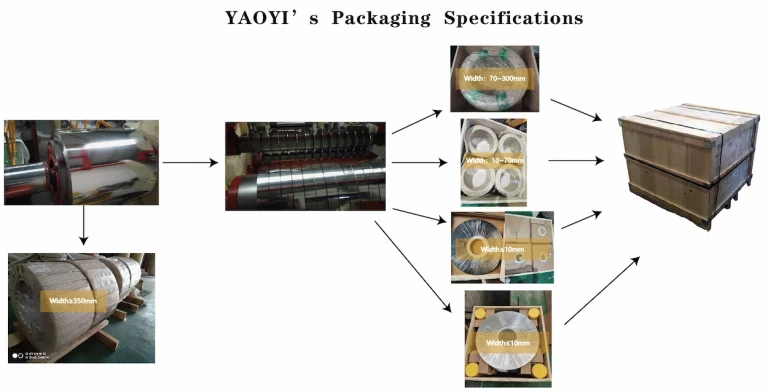
YAOYI is a cold-rolled stainless steel manufacturer established on March 12, 1996. We produce and process 201, 304, 316L and other stainless steel strips. Among them, 304 and 316L are more frequently purchased by customers. Due to 304 and 316L are also the most common steel grades in the market due to their excellent rust resistance and machining performance.
Compared with Cr-NI stainless steel 304, the performance of 316L stainless steel is greatly enhanced in chemical corrosion performance. In addition, SS316L also has better resistance to high-temperature creep, stress fracture, and tensile strength than other steels. It is convenient to control the quality of raw materials for your products and minimize metal impurities.
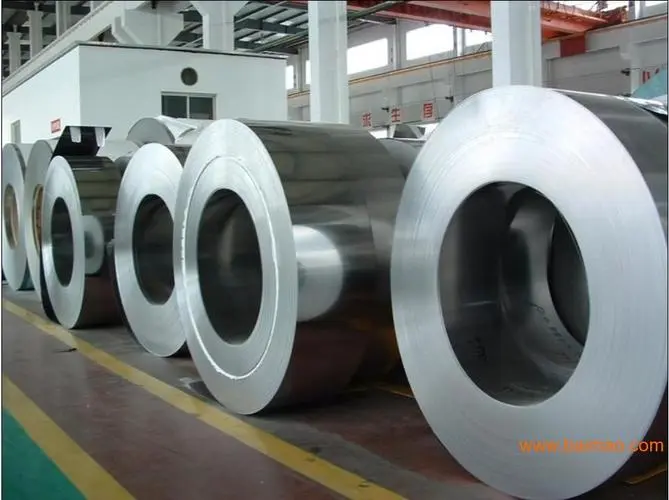

The SS 316L produced by yaoyi can be processed into pipes, sheets, plates, and strips with its excellent performance. When your product needs to work in an environment resistant to high oxidizing acid corrosion, the aisi316L stainless steel produced by yaoyi is more resistant to corrosion than other ordinary Cr-Ni stainless steel without Mo. All in all, we can help you with product quality control.
|
Different media |
316 stainless steel is stainless steel made by adding some molybdenum to pitting corrosion resistance of 304 stainless steel. Moreover, in various types of water (distilled water, drinking water, river water, boiler water, etc.), the corrosion resistance of 304 stainless steel and 316 stainless steel is almost the same, but when the content of chloride ions in the medium is very high, 316 stainless steel is more suitable. |
|
Different price |
316 stainless steel is more expensive than 304 stainless steel due to the molybdenum and nickel elements added in 316. |
|
Different chemical composition |
304 is cover type stainless steel, material composition is OCr18Ni9, however, 316L is austenitic stainless steel, material composition is OOCr12Mo2Ti. |
|
Different maintenance methods |
304 has better corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance and processability than 316 stainless steel. |

Stainless steel is a group of iron-based alloy that proves to be versatile, widely used due to its durability and high corrosion resistance. The Grade 316L stainless steel properties give manufacturers the freedom to shape and roll steel to desired forms for various applications. Additionally, it is aesthetically appealing, hygienic, and easy to maintain.
The Grade 316L stainless steel is a molybdenum-bearing austenitic stainless steel, which is known to be to be the most commonly used stainless steel in the market. As it is stainless steel, 316L steel features longevity that meets the requirements of sustainable construction.
Furthermore, it does not leach compounds that could change its composition when in contact with elements. This article will tell you everything there is to know about 316L stainless steel, particularly its properties and application.

The 316L is generally known as the low carbon version of the grade 316 stainless steel. 316L is proven to more resistant to corrosion, as well as both crevice and pitting corrosion than conventional steels. It is immune from grain boundary carbide precipitation, making it very useful in applications that require welding, particularly in heavy gauge (over 6mm). The 316L steel also offers higher creep, stronger at high temperatures, and higher stress to rupture.
Grade 316L is primarily used in process streams containing halides or chlorides. It also gives high-quality formidability and fabricability to manufacturers, enabling them to form the steel for various fits and applications.
You can identify grade 316L stainless steel by looking at the carbon levels. It should have lower carbon when compared to the grade 316 steel. Furthermore, it is an austenitic stainless steel, which is defined by its face-centered cubic crystal structure. Below are some of the grade 316L’s properties that can distinguish it from every other grade steel.
The Grade 316L has a density of 8000 kg/m3 and an elastic modulus of 193 GPa. At 100°C, it has thermal connectivity of 16.3 W/m.K and 21.5 W/m.K at 500°C. The 316L also has an electrical resistivity of 740 nΩ.m, with a specific heat capacity of 500 J/kg.K.
The Grade 316L has a minimum tensile strength of 485 and minimum yield strength of 120 at 0.2% proof of stress. It features an elongation of 40% in 50mm/min and maximum hardness of 95kg under the Hardness Rockwell B test. Under the Brinell scale test, the grade 316L steel had a maximum hardness of 217kg.
The Grade 316L has maximum carbon levels of 0.030%, while its silicon levels sit at a maximum of 0.750%. Maximum manganese, phosphorus, nitrogen, and sulfur levels are at 2.00%, 0.045%, 0.100% and 0.030%, respectively. It is made up of chromium levels at 16% min and 18% max, while its nickel levels are at 10% min and 14% max. Meanwhile, its molybdenum levels have a minimum level of 2.00% and a max of 3.00%.
It is generally more resistant to corrosion than Grade 304 steel. Grade 316L proves to be excellent in various corrosive media and atmospheric environments. It can also be subject to crevice and pitting corrosion in warm chloride situations. Furthermore, it has proven to stay intact even under stress corrosion cracking tests at above 60 °C. Tests also confirmed that 316L is resistant to water with up to 1000mg/L chloride levels.
However, 316L steel is not resistant to warm seawater. This is similar to its Grade 316 counterparts, despite being regarded as the standard “marine grade” stainless steel.
It has proved to stand annealing of heats to 1010-1120°C and cools rapidly. However, thermal treatments cannot harden the 316L steel. It does give excellent oxidation resistance in intermittent service to 870°C to 925°C. It also proves to be more resistant to carbide precipitation. Manufacturers can also continuously use the Grade 316L in temperatures within the 425-860°C range.
If machined too quickly, the 316L would tend to work hard. Manufacturers should handle this grade steel with low speeds and constant feed rates. Despite this, it is generally easier to machine than 316 steel because of its low carbon levels. You cannot weld it using oxyacetylene methods. It is, however, a choice that most consumers prefer when seeking weld fillers.

The 316L can be used extensively for weldments due to its immunity to carbide precipitation. It can be shaped into various forms and products such as sheets, coils, and strips. Grade 316L stainless steel features high molybdenum levels.
Due to this component, the 316L can be considered “marine grade,” making it safe and preferable for environments that are rich in chloride like the sea and coastal regions. 316L can also be considered one of the standard medical-grade stainless steel. Thus, it is perfect for use in the medical field, particularly in chemical and pharmaceutical applications.
Stainless steel products made from grade 316L can also be used in the food industry. The 316L features a chromium-nickel composition and high corrosion resistance, making this an ideal material for food-related applications. As it does not tarnish or rust easily, many kitchenware and tableware are made of stainless steel. Notably, the 316L would fit well in applications that have intense requirements in corrosion and chemical resistance.
It is preferably effective against acidic environments too. The 316L can be used for parts that will stand corrosion caused by acetic, formic, hydrochloric, sulfuric, and tartaric acids. Moreover, it can also withstand corrosion brought by alkaline chlorides and acid sulfates. Other uses for the 316L steel include the construction of exhaust manifolds, photographic equipment, and furnace parts.
Listed below are some of the most common applications for grade 316L steel:
●Architectural application
●Condensers, tanks, and evaporators
●Equipment for food preparation
●Pollution control
●Boat fitting, value, and pump trim
●Marine applications
●Laboratory equipment
●Pharmaceutical industries
●Chemical processing for inks, photographic chemicals, and rayons
●Heat exchangers
●Fasteners

When using grade 316L stainless steel, there is no need to worry about any tarnish or rust. It does not contain lead and cadmium and is generally considered hypoallergenic. All of these are factors that cause other steel types to tarnish and rust. Its molybdenum components enhance the steel’s ability to resist corrosion in environments with high salt and chloride levels. As long as its passive layer remains intact, it will stay stainless and corrosion-free.n in environments with high salt and chloride levels. As long as its passive layer remains intact, it will stay stainless and corrosion-free.
The L in 316L means low carbon content, which serves as the main difference between the two stainless steels. The lower carbon levels meant that 316L is softer than 316, resulting in many differences in corrosion resistance, weldability, and machinability.
316L grade is easier to weld. Manufacturers can easily weld this with other metals or steel with little to no issues. 316L steel can also be easily shaped into any form. On the other hand, 316 is very susceptible to weld decay. 316L is also more resistant to corrosion than 316.
If used in everyday applications, you may not see many differences. This resistance is more apparent when weldability is concerned. While welding 316 will require annealing, the 316L will prove to be valuable and resistant against corrosion without additional steps.
Although 316L provides better corrosion resistance, the 316 grade still has better mechanical properties. The 316 gives manufacturers more rigid steel, higher tensile strength, and more ductile compared to 316L.
Despite these differences, both stainless steels are very malleable. They are both useful when forming the shapes necessary for any project without breaking or even cracking. Once properly formed, both steel grades have high resistance to corrosion and high tensile strength.
The L in 316L means low carbon content, which serves as the main difference between the two stainless steels. The lower carbon levels meant that 316L is softer than 316, resulting in many differences in corrosion resistance, weldability, and machinability.
316L grade is easier to weld. Manufacturers can easily weld this with other metals or steel with little to no issues. 316L steel can also be easily shaped into any form. On the other hand, 316 is very susceptible to weld decay. 316L is also more resistant to corrosion than 316.
If used in everyday applications, you may not see many differences. This resistance is more apparent when weldability is concerned. While welding 316 will require annealing, the 316L will prove to be valuable and resistant against corrosion without additional steps.
Although 316L provides better corrosion resistance, the 316 grade still has better mechanical properties. The 316 gives manufacturers more rigid steel, higher tensile strength, and more ductile compared to 316L.
Despite these differences, both stainless steels are very malleable. They are both useful when forming the shapes necessary for any project without breaking or even cracking. Once properly formed, both steel grades have high resistance to corrosion and high tensile strength.
The density of 316L stainless steel is about 8,000 kg/m^3 or 8 g/cm^3. It’s important to note that this density remains almost constant in different environments and varying temperatures, making 316L an excellent material for various applications.
Poisson’s ratio for 316L stainless steel is typically around 0.25 to 0.33 at room temperature. Poisson’s ratio is a measure of how much a material compresses in one direction when it’s stretched in another, which is a critical property to understand when designing components.
The hardness of 316L stainless steel affects its formability, machinability, and wear resistance. While it’s not as hard as some other types of steel, its relatively high toughness and ductility make it a versatile material for various applications. It’s crucial to consider hardness alongside other properties like yield strength and corrosion resistance when choosing a material for a specific application.
Both SS 316 and SS 316L are molybdenum-bearing austenitic stainless steels. The primary difference lies in their carbon content. SS 316 has a maximum carbon content of 0.08% while SS 316L (L stands for “Low carbon”) has a maximum carbon content of 0.03%. This lower carbon content in SS 316L gives it an increased resistance to sensitization, making it ideal for welding applications.
The density of 316L stainless steel is approximately 8000 kg/m3. This can slightly vary based on the specific composition and manufacturing process. However, this density allows 316L stainless steel to have excellent toughness, even at cryogenic temperatures.
The hardness of 316L stainless steel can vary based on its heat treatment. However, its typical hardness in the annealed condition is around 149 HB (Brinell Hardness).
The Poisson’s ratio for 316L stainless steel is typically around 0.3. This value, which ranges between -1 and 0.5 in a stable, isotropic material, is a measure of the deformation in the transverse direction to the applied load relative to the deformation in the direction of the applied load.
The yield strength of 316L stainless steel is approximately 170 to 220 MPa. This can vary depending on the exact processes the material has undergone.
AISI 316L is the American Iron and Steel Institute’s designation for a particular type of stainless steel. This grade is a low carbon version of AISI 316, with the ‘L’ signifying its low carbon content. This results in a steel with excellent corrosion resistance, particularly against chlorides and other industrial solvents.
Grade 316L stainless steel is an excellent material that manufacturers can use in a variety of industry applications. It mainly sees high demand in environments that demand immense resistance to chemicals and corrosion.
This resistance is why manufacturers use 316L grade stainless steel in the marine, pharmaceutical, and food industries. It is also generally the pick when welding and forming parts. Before purchasing 316L stainless steel, it is essential to note its properties and applicability to see if it fits your project.
You may contact us for further inquiries regarding 316 stainless steel coils. Yaoyi takes pride in delivering only high-quality products and services.