Myriad is an expert in Steel Grade 304 stainless steel, you can rely on us and we will be your best AISI 304 material raw material supplier and partner in China. The ASTM 304 stainless steel food Grade is widely used in the kitchen and so on. Product specifications define the specific criteria. ASTM 304 stainless steel is acceptable as long as the Ni content is greater than 8% and the Cr content is greater than 18%. This is why this form of stainless steel refers to 18 / 8 stainless steel in the industry.
Produce 0.02mm~20mm cold rolled 304 ss coil.
Square tubes, round tubes, U-shaped tubes, special-shaped tubes, etc. are available.
We can cut out the stainless steel plate of the specifications.

The cold-rolled coil is an intermediate semi-finished product. Its raw material is 304 hot rolled coil, and its downstream products are astm 304 ss plate and 304 ss pipe. Therefore, while we can provide various thicknesses of 304 ss coils, we can also provide you with high-quality 304 ss derivatives. Including 304 stainless steel plate, tube, and hot rolled coil.
We have long-term cooperation with many steel mills, so we can get 304 stainless steel hot rolled coil with very high-cost performance. At the same time, we also provide 304 cold-rolled stainless steel coils for many astm 304 ss pipe factories, so we can also provide the most cost-effective 304 ss pipes to save your raw material procurement costs and time and achieve one-stop procurement.
Are you looking for the most comprehensive supplier of 304 stainless steel? Or you are clean about using 304 stainless steel in your production? We have made this guide for you to introduce the information you need. This guide can help you to know more about the process of purchasing and using 304 ss, and save your time.
Ever wondered what the most popular types of stainless steel are? The quick answer to this is austenitic steel, and there might even be a chance you have heard of that term before. If not, you are in the right place!
Purchased 304 hot-rolled coil from the best quality steel plant.
The finished product is cut to the size you need.
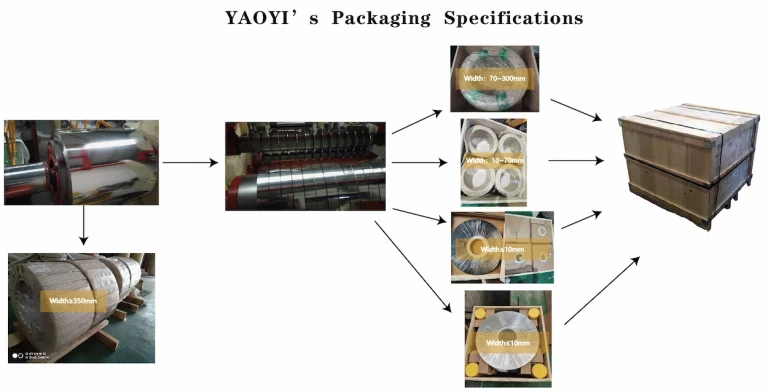
We ensure that your goods have the best packaging protection.
To ensure that your product quality meets your requirements.
1. Due to our contract price with the steel plant, we can lower the quotation below the market average.
2. Since we supply stainless steel pipe factories, you can get the lowest quotation in the market and have quality control.
3. We can provide you with 0.02mm thick 304 ss foil, and meet your LOW MOQ requirements.
4. With 25 years of experience in stainless steel production, we have accumulated strong research and development capabilities to meet your technical requirements.With a large storage area of 5.53 acres, we can provide you with free storage services in China.

AISI 304 material is stainless steel formed for primary shaping into wrought items. For this stuff, 304 is the AISI designation. The UNS number is S30400. Furthermore, 304S15 is designated as British Standard (BS). And the appellation AFNOR (French) is Z7Cn18-09.
Therefore, an austenitic chromium-nickel stainless steel is commonly used in AISI 304 material (1.4301). It is also highly corrosion-resistant with excellent drawing and high formability. Typical applications of 304 stainless steel are sinks, kitchen appliances like panels, tubing, and more.
Conversely, the AISI 304 is also often called 18/8, a moniker from its usual 18% chromium and 8% nickel composition. Nickel, manganese, silicon, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, and sulfur are other components of the alloy.
Besides, the charts of the material properties cards compare AISI 304 material stainless steel with the wrought stainless stones (tops), all iron alloys (middle ones), and the whole database. Besides, the charts on AISI 304 material material properties can be compared (bottom). A complete bar implies that this is the highest value in the package. A half-full bar means 50% higher, and so on.
304 austenitic stainless steel has excellent cold workability and formability, corrosion resistance, resistance to intergranular corrosion, in addition to good welding performance, and has good mechanical properties in low temperature situations. Its yield strength at room temperature is not less than 231 MPa, its tensile strength is greater than 520MPa, and its elongation after fracture is 60%.
The two main stainless steel grades are 304 (known as ‘A2’) and 316. (known as A4). Both of these grades provide great resistance to corrosion, cleanliness, and handling of very low (cryogenic) and high temperatures.
Grade 316 is thus also known as marine stainless steel due to its gradual corrosion resistance to chloride compared to type 304.
First, Grade 304 in steel (A2): 18% chromium + nickel (’18/8′). 316 grade stainless steel: 18% chromium, 8% nickel, 3% molybdenum.
Next is the crystalline structure of oxidated steel, determined by its chemical composition, which can also be graded. The above two grades are austenitic stainless steel. Ferritic, Martensitic, Duplex are other types.
Stainless steel is the most frequently used stainless steel grade 304. The stain comprised chromium (between 18% and 20%) and nickel, the main non-iron parts of metal (between 8 percent and 10.5 percent ). This is austenitic stainless steel.
The Ni factor in the composition of ASTM 304 stainless steel is very significant, as it directly defines the corrosion resistance of ASTM 304 stainless steel and its value. Ni and Cr are the two most significant elements in 304, but they are not the only ones.
The applicable quality specifications have very specific requirements for 304, with some variations for various shapes of stainless steel.
Moreover, the electric and thermal conduction is less than carbon steel and magnetic, but less than steel. The corrosion resistance is higher than normal steel. The ease with which it is information in different forms means that it is commonly in use.
On the other hand, SAE International specifies it as part of its steel classification SAE. In compliance with ISO 3506 for fasteners, the A2 is widely in use outside of the United States as stainless steel. It is in application to 18/8 stainless steel in the commercial cookware industry. UNS S30400 is part of the unified numbering scheme. This material is similar to SUS304 in Japan. The European standard 1.4301 also stipulates it.
Furthermore, the stainless steel 304 and steel 304L classes are famous as the 1.4301 and 14307. The most versatile and widely used stainless steel is Type 304. It is still known at times with its old 18/8 name which comes in the form of a nominal composition of type 304 with 18% chromium and 8% nickel. Type 304 is a grade of austenitic that can be severely noticeable.
In applications such as sinks and casseroles, 304 was thus the main grade in usage. Type 304L’s low carbon variant is 304. It is in use for enhancing weldability in heavy gauge parts. Certain items including plates and pipes may be available in “dual approved” material, which satisfies both 304 and 304L requirements. Also available for use at high temperatures is a high carbon content version 304H.
Read on 316L Stainless Steel Properties
Strip
Bar
Platform Plate
Tube
Can Pipe
Bow
Steel grade 304 provides a wide range of ambient environments, corrosive surfaces, and excellent strength. Cracking and cracking at a temperature of over 60°C in warm chloride conditions. It’s corrosion-prone. It can contain up to 400 mg/l chlorides and is known to be corrosion resistant in water at ambient temperatures, reducing to around 150 mg/L at 60°C.
Thus steel grade 304 also is highly susceptible to thiosulfate anions, emitted by room temperature, since they happen in acid mine drainage and may be subject to severe pitting problems when in contact close contact with pyrite or sulfide-rich clay materials exposed to oxidation.
If the steel grade 304 in acidic applications is too vulnerable to chloride pitting or crevice corrosion, it is usually in 316 stainless steel for more severe corrosion conditions.

AISI 304 material possesses a very high corrosion resistance, is non-magnetic, and cannot be thermally decided.
Since SS 304 can withstand very corrosive environments it is relatively easily formed, processed, and welded, which is ideal for material handling.
Finally, the most common kind of stainless steel currently used is SAE/ANSI 304 (AISI 304 material). It is popular among several applications including automotive parts, vaporizer coils, electric components, and medical equipment.
Steel grade 304 is well resistant to oxidation when used intermittently, up to 870°C and continuous operation up to 925°C. It cannot, however, be used continuously at 425-860°C in a recommendation. In this situation, 304L is recommended because of its resistance to carbide precipitation. When high temperatures above 500°C are needed, and at 304H grade, 800°C is sufficient. It maintains an aqueous corrosion resistance.
MAnufacturing steel can only be manufactured with stainless steel machines. Before usage, tool and work surfaces must be cleaned attentively. These steps must be taken to prevent cross-contamination of stainless metals from the corrosion of the produced product surface quickly.

AISI 304 material’s Achilles heel is chloride and high-temperature environment (above 60 degrees Celsius). This can result in cracking and general damage to the protective layers of the steel in these conditions.
However, SS 304 remains suitable for a broad variety of applications because chloride can generally only be found in controlled environments and at relatively low concentrations. No surprise, along with the highest class SS AISI 316, this is the most popular stainless steel available today.
Of course, AISI 304 material will indicatively stand up to temperatures up to 925o Celsius with sufficient strength and resistance to corrosion.
One of the most public precipitation hardening grades available. It is capable of high properties with a single precipitation or aging treatment when soft and ductile in the solution annealed state. Corrosion resistance, high hardness, toughness, and strength are all characteristics of this material.
Stainless steel manufacturing 304 needs care and accuracy. There is a certain degree of precision in the concentration of the different components forming SS 304. As a result, even the instruments used to make the SS AISI 304 material need to be cleaned thoroughly in advance.
Subsequently, if the production is carried out with the cold process, a rinding step must be completed before the completion is completed. This reduces the chance of ruptures and ruptures. Forging with a temperature of up to 1260 degrees Celsius can be accomplished when the hot process is used. In a solution, the corrosion resistance, ductility, and strength are then instantly cooled.
Stainless Steel Foil Manufacturer
AISI 304 material is strongly oxidizing acid resistant to corrosion. In chloride environments, however, corrosion can occur. 304 stainless steel, like 316 stainless steel, is not as corrosion-resistant.
However, its low thermal conductivity means that coolants and lubricants are to be used freely, especially at the cutting edges.
The following principles can be in use to improve machining:
Sharply from the edges. Turtle frontiers allow so much work to harden. Light but deep enough cultures should be generated so that the material surface can not harden. To ensure that the swarf remains clear, chip breakers should be used.
Authentic alloys, besides, have low thermal conductivity and lead to heat levels at the edges of the cut. Therefore, coolants and lubricants are essential in large quantities and should be used.
Heat treatment in 304 is not allowed to heat cure. The cooling or cleaning can be completed quickly after heating it at 1010-1120°C.

|
C |
Mn |
P |
Cr |
Ni |
S |
Si |
|
≤0.03 |
≤2 |
≤0.045 |
18~20 |
8~12 |
≤0.03 |
≤1 |
1.The normal maximum carbon percentage is 0.07
2.The standard specified maximum percentage of manganese is 2
3.The maximum phosphorus percentage is 0.045304 in the norm.
4.The regular sulfur maximum percentage is 0.03
5.As specified in the norm, the maximum Silicon percentage is 1
6.Nickel as specified in the norm has a maximum proportion of 11
7.The maximum chromium level as specified in the standard is 19 while the minimum chromium level as defined in the standard is 17.
High temperature resistance 800℃,
Tensile strength σb (MPa) ≥ 515-1035,
Conditional yield strength σ0.2 (MPa)≥205.
Elongation δ5 (%)≥40
Reduction of area ψ (%)≥60
Hardness ≤187HB, ≤90HRB, ≤200HV
Density 20℃ g/cm3
Melting point (℃): 1398~1454
1.The maximum hardness in HB is 201.
2.The minimum strength of the traction is 515 Mpa.
3.Yield intensity is 205 Mpa.
4.The normal elongation is 40% in 50mm.

1.The JIS regular equivalent material is called SUS 304 steel.
2.The material in the DIN standard is referred to as 1.4301 steel.
3.The analog material is referred to as steel type S30400 in the UNS standard.
A Manufacturer of Stainless Steel Strips
First, AISI 304 material has almost the same chemical alloys as 303 stainless steel except for the carbon difference. In 303 stainless sheets of steel, AISI 304 material has a lower carbon content i.e. 0.07% compared to 0.12% Carbon. It makes it less difficult and manipulative for form 304.
On the other hand, 316 stainless steel has almost all chemical specimens equal to 304 stainless sheets of steel except molybdenum, which in saline environments renders it corrosion protective. The nearest match to grade 304 is 316 stainless steel.
In the classifications, stainless steels such as austenitic, ferritic, martensitic, duplex, ferritic, and austenitic blend and PH – hardening of precipitation (martensitic, semi-austenitic, or austenitic). AISI 304 material and have an austenitic microstructure such as 90% of the nickel content of stainless steel consumed.
1.Excellent resistance to corrosion in natural or slightly violent conditions
2.Excellent efficiency at low temperatures
3.High-temperature output
4.Easily toiling
5.Good ductility and fitness
6.Outstanding solderability
7.Great hygienic condition suitability
8.Non-magnet.
The mechanical properties table of stainless steel shows that while the yield strength of AISI 304 material and AISI 316 can be similar to structural steels, standard tensile strength stones are superior to those of the steels. Nonetheless, neither alternative is ideally suited to the reliability of abrasives and hard wear. Wear-resistant stones such as Hardox are the perfect solution.
The same hardness values (Brinell), elastic modulus, and tensile strength are found in AISI 304 material and 316. The yield strength of AISI 316 is much higher at 200 MPa (1450°C vs. 1 400°C at 316), whereas the melting point of the AISI 304 material is marginally higher (1400% MPa at 304). The corrosion resistance of the AISI 316 is generally better than 304.
For this 304 Stainless Steel, the relevant millimeter thickness is between 0.25 and 6.25, while the millimeter width is between 600 and 1200.
1.Bobbins
2.Cutting papers
3.Square, hexagonal, circular, and flat bars
The rust prevention & control mechanism of type 304 is robust. The product is used for the production of food and kitchen appliances. It is corrosion from the highest oxidizing acids.
However, chloride corrosion is especially susceptible to saline air, which has exceptional amounts of sodium chloride ‘NaCl.’ Chloride ions may produce limited corrosion areas, called “pitting” that can blow under the chromium fence under defensive conditions to break the arrangements of the inner building materials.
Stainless steel ASTM 304 is commonly in use in both commercial and residential applications. In the medical device industry, ASTM 304 is in use in applications that require high corrosion resistance, formability, strength, manufacturing precision, durability, and hygiene.
Application Of Stainless Steel In The Oil And Gas Industry
1.Various Applications – can be in use for a variety of medical devices – economies of scale – raw material costs are reduced.
2.Rust Evidence – decreases the risk of contamination caused by rust and other oxidation-related surface imperfections.
3.Corrosion Resistance at a High Level
4.Recyclable materials
5.Antibacterial properties
6.It does not stain, so it can be washed and reused in the medical field several times.
7.Non-magnetic – ideal for operating rooms and body implants. High heat resistance
8. Stainless Steel ASTM 304 will retain its shape after it has been work-hardened.
Their corrosion resistance is known as inoxidable steels. The combination of power and low servicing makes them suitable for a large number of applications.
In the same manner, it is used all over the place from buildings and buildings to medical equipment and food. Avoidance of rust may also be a matter of the durability of a building. Corrosion will consume metal, and the load-bearing capacity of your construction will decrease over time.
Meanwhile, temperature changes can affect corrosion greatly. It speeds up the operation, making conditions more difficult. In such a setting, stainless steels are suitable. Far more than structural coated steels, since the coating is destroyed more easily in such a situation.
Application of Stainless Steel in Marine Installations
1.Cannula clamps medical instruments parts and handles
2.Equipment for food processing
3.Transport tanks for petroleum products
4.Kitchen sinks and various kitchen utensils
AISI304 is very common for a wide range of applications, as it can withstand extreme corrosive environments and can also be molded, machined, and welded reasonably easily:
1.AISI 304 material kitchen sink in stainless steel
2.Car components such as exhausts
3.External building
4.Spray
5.Screws, nuts, and bolts are industrial parts
6.Bottling springs Springs
7.Washing machine Kitchen
8.Pans for cooking
9.The pipe
10.Sections of the brewery
11.Components for power generation
12.Processing units for chemical products
13.Medical facilities
There are more explanations why 304 is used in the above sectors. These include the esthetic look, easy washing, relatively high strength to weight ratio, and high availability in many various types.
Stainless Steel Application of Medical Treatment
1.Orthopedic implants are made of precision stainless steel tubing (predominantly 316 / 316L).
2.Artificial heart valves (predominantly made of 316 / 316L stainless steel)
3.Fixation of the bones
4.Mandrels and other instruments
5.Hazardous waste containers / Chemical containers
6.Coils of wire
7.Forms made of wire
8.Guidewires for a specific purpose
9.Curettes are a form of curette that is
10.Plates, screws, and prostheses
11.Needles for medical use
12.Syringes for medical use
13.Probes for sensors
14.Catheters
15.Otolaryngology
16.Sinks, pots, surfaces, trays, and knives
Therefore, simple to work with Cold Working steel grade 304. Cold work methods may require an intermediate rinsing phase to reduce hardness and prevent tearing or cracking. A full ringing operation should be in use to minimize internal stress and optimize corrosion resistance when the manufacturing is in full completion.
Manufacturing methods such as forging can take place after uniform heating at 1149-1260°C, with hot working. To ensure optimum corrosion resistance, the manufacturers’ components should be quickly in preparation.
n connection, ASTM 304 Stainless Steel is the standard “18/eight” stainless steel; it is the most flexible and widely used stainless steel, available in a wider variety of products, varieties, and finishes than any other.
For full martensite transformation, soak for 30 minutes at 1900 degrees Fahrenheit (1038 degrees Celsius) and then cool to below 60 degrees Fahrenheit (16 degrees Celsius).
Next, soak the substance in the solution for four hours at the quantified temperature, then air dry.
And lastly, soak solution-treated material at 1400 degrees Fahrenheit (760 degrees Celsius) for 2 hours, the air cold, then re-heat to 1150 degrees Fahrenheit (620 degrees Celsius) for four hours, air cool.
This alloy can be successfully in weld using traditional fusion and resistance methods, but oxyacetylene welding is not advisable. If filler metal is in need, AWS E/ER630 is in a recommendation.
Before forging, soak for 1 hour at 2150 F (1177 C). Do not work below 1850 degrees Fahrenheit (1010 C). Before final hardening, after-work solution treatment is in need.
The machinability of this alloy is considered by long, gummy chips. You can machine it in the annealed state, but the H1150M state produces the best results. If machining in this state, post-machining solution treatment of parts will be in need before final hardening.
On the other hand, spring-type functions, higher strength, cold-worked conditions may also be in the definition for Type 304/304L. In the annealed state, Type 304/304L is non-magnetic, but cold working will cause it to become barely magnetic.
Whereas ASTM 304 and Type 304L have chemical and mechanical properties that are somewhat similar, and they are often in combination on a single materials examination certificate when the exact properties of a chrome steel plate match the factors of both varieties.
How to Buy Stainless Steel Coil Springs Raw Material?
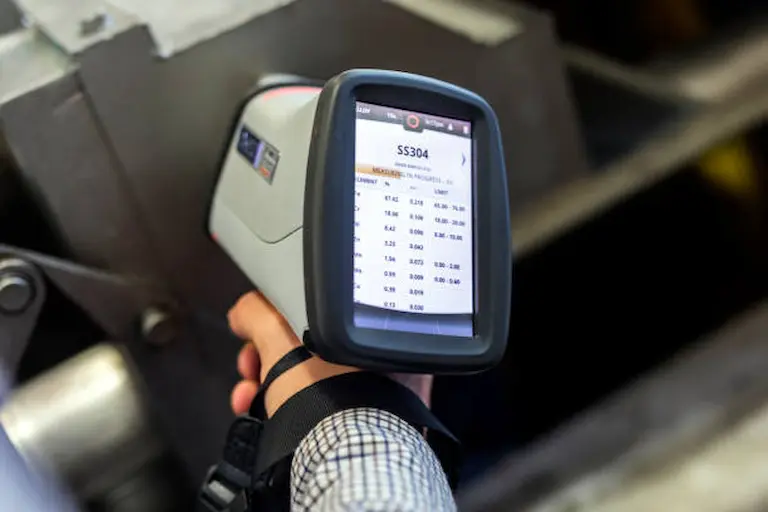

1. Purchase quantity and required delivery time.
2. 304 ss coil hardness requirements, specifications (width and thickness), surface, tensile strength.
3. If you can’t confirm the hardness you need, you can tell us your application. We have an experienced team of engineers who can recommend suitable 304 ss for you according to your application.
4. 304 ss packaging requirements.
After clarifying these needs, you can find suppliers through the B2B website or the factory website. It is worth reminding that many b2b platform vendors are not manufacturers. Their advantage is service, but they have little knowledge of product expertise. If the 304 ss coil you need has small technical requirements and pays more attention to the price (this kind of stainless steel coil is called a general product in the industry), you can find them. Because they usually have multiple suppliers and can provide you with low prices, but the quality cannot be maintained consistently and the quality control is not good.
STAINLESS STEEL APPLICATION OF STAINLESS STEEL WASHER
If you are in the machining industry, you need to purchase 304 ss coils that require high technology and quality. I suggest you directly choose the 304 ss manufacturer. Such as yaoyi. We can provide you with the most professional stainless steel solutions.
Usually, you need to confirm which factory the hot-rolled material of this manufacturer is used for? Because in China, there are several levels of hot-rolled coil suppliers: the top: Baosteel, TISCO, TSINGSHAN, POSCO; the second category: Fuxin, ansteal, JISCO, lewar. The third category: some small steel plants (quality cannot be guaranteed).
If you buy stainless steel pipes, you need to confirm their production process. If you are purchasing seamless pipes, you must choose pipes that have undergone bright solution annealing and leveling in the core rod. The thin-walled stainless steel pipes produced by these processes are corrosion-resistant, aging-resistant, high-precision steel pipes, well-balanced wall thicknesses, and smooth inside and outside surfaces. High brightness, of course, the most accurate judgment of the quality of the steel pipe, a series of tests are needed.
Finally, after the production of your order is completed, you can ask the stainless steel manufacturer for their inspection report. If a formal factory, they will all have a laboratory. In this report, you can confirm the material and physical properties of stainless steel. We have been focusing on producing 304 ss cold rolled coil for 25 years. The cold-rolled coil is an intermediate semi-finished product. Its raw material is 304 hot rolled coil, and its downstream products are 304 ss plate and 304 ss pipe. Therefore, while we can provide various thicknesses of 304 ss coils, we can also provide you with high-quality 304 ss derivatives. Including 304 ss plate, 304 ss tube, 304 hot rolled coil. We have long-term cooperation with many steel mills, so we can get 304 ss hot rolled coil with very high-cost performance. At the same time, we also provide 304 cold-rolled stainless steel coils for many 304 ss pipe factories, so we can also provide the most cost-effective 304 ss pipes to save your raw material procurement costs and time and achieve one-stop procurement.
Yaoyi is an expert in Steel Grade 304 , you can rely on us and we will be your best stainless steel raw material supplier and partner in China.
Read more about 304 Stainless Steel Sheet: Technicalities, Features and Applications
Learn more about 316 Stianless Steel
304 ss is austenitic stainless steel and is widely used daily. But because it contains the Ni element, the price is relatively high. Some unscrupulous suppliers will use two types of stainless steel to replace 304. One type is 400 series ferritic stainless steel, which does not contain Ni. The other is 200 series austenitic stainless steel that use Mn instead of Ni. It is worth mentioning that 201 stainless steel can indeed replace 304 ss under certain circumstances.
The stainless steel identification potion is mainly identified by corroding the surface of the stainless steel to free the components on the surface of the stainless steel to react with the substance in the detection potion to show different colors! After the inspection, the stainless steel is locally corroded, and the passivation film is destroyed. It may be easier to precipitate heavy metals such as chromium and nickel during use. This type of method is used to determine whether your supplier uses 201 stainless steel instead of 304 ss.
Get it now:AISI 302 Stainless Steel
This is the easiest way. Here is another type of replacement for 304 ss-400 series stainless steel. 400 series stainless steel is ferritic stainless steel with magnetic properties, while 304 ss is mostly non-magnetic or weak magnetic stainless steel.
The stainless steel identification potion is mainly identified by corroding the surface of the stainless steel to free the components on the surface of the stainless steel to react with the substance in the detection potion to show different colors! After the inspection, the stainless steel is locally corroded, and the passivation film is destroyed. It may be easier to precipitate heavy metals such as chromium and nickel during use. This type of method is used to determine whether your supplier uses 201 stainless steel instead of 304 ss.
Use precision instruments such as inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES), X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF), carbon-sulfur analyzer, scanning electron microscope, and energy spectrum analyzer (SEM+EDS) to analyze all elements of metal materials Perform qualitative, semi-quantitative, and quantitative analysis with all ingredients, and perform metal brand identification and element analysis according to American standards, ISO international standards, national standards, European standards, German standards, and Japanese standards.
Keep reading: A complete guide to AISI 303 Stainless Steel

304 stainless steel has the characteristics of strong corrosion resistance, high-temperature resistance, low-temperature resistance, high toughness, easy processing, and so on. There are many determinants of the service life of 304 ss.
If you are in an inland area and the working environment of the purchased 304 ss is a weak acid, weak alkali, and constant temperature environment, and you can properly maintain and clean up during use, 304 ss can be at least 70 years old.
If the use environment of 304 ss is a strong acid, strong alkali, or long-term high temperature and low-temperature conditions, the service life of 304 ss will be about 30 years.
If the 304 ss you purchase is produced in a regular factory, there are few impurities in the stainless steel production process, which will greatly extend the life of 304 ss.
If you are using 304 ss, regular cleaning and maintenance will also greatly extend the use time of 304 ss.

Two factors affect the hardness of 304 ss: annealing treatment and carbon content.
The first factor is that the annealing treatment of 304 ss removes the strengthened cold work stress during cold rolling. The original hard plate becomes softer, but its hardness still reaches the national stainless steel standard.
The second factor is that the carbon content of 304 ss is less than 0.07%. Carbon is responsible for improving the hardness of stainless steel, but carbon is an impurity for stainless steel. The more the content, the harder the hardness, the chance of rusting of 304 ss Will be bigger.
There are three types of the hardness of 304 ss: soft, 1/2 (half-hard) hardness, and full-hard.
The 304 full-hard stainless steel belt has a Vickers hardness of 370°-600°, it is often used for architectural decoration, heavy oil burner parts, etc.
The 304 semi-hard stainless steel means it has a Vickers hardness of 250°-370°. It has good mechanical properties, deep drawing, and good elasticity. 304 semi-hard stainless steel belt is widely used in springs, hardware accessories, machining, and other fields.
At last, 304 soft stainless steel strip refers to annealed stainless steel. This type of 304 ss has a very wide range of applications, and most of the 304 ss we see in daily life are of this kind. Its hardness is less than 210HV.
Try for free information about the A Complete Guide to AISI 321 Stainless Steel
Hardening of 304 ss requires the process of cold rolling. Cold rolling refers to a material processing method in which the steel strip is rolled at room temperature to gradually reduce the thickness of the steel strip. The raw material for cold rolling is generally hot rolled and annealed steel coils. During the cold rolling process of 304 ss, the metastable austenite structure will undergo strain-induced martensitic transformation, which will increase the strength and hardness of the steel and decrease the plasticity, resulting in obvious.
Get it now:A complete guide to AISI 410 Stainless Steel
As the number of rolling passes increases, the total rolling deformation rate increases, the work hardening effect becomes more and more obvious, and the material becomes harder and harder. The 304 hot-rolled coil in the conventional annealed state has lower strength and hardness and better plasticity, which is good for rolling.
The main mechanisms of work hardening include dislocation strengthening, grain boundary strengthening, secondary phase particle strengthening, and strain-induced phase transformation strengthening. In fact, strengthening is not determined by a single mechanism. In most cases, it is the result of a combination of several mechanisms.
With the increase of engineering strain, the yield strength σ0.2, tensile strength σb, hardness HV and yield ratio σ0.2/σb all gradually increase, and the elongation gradually decreases, indicating that as the amount of deformation increases,304 austenitic stainless steel has produced obvious work hardening, the strength and hardness indexes are significantly improved, and the plasticity is reduced.
Try for free AISI 4140 Low Alloy Steel

The rust of 304 ss occurs because it comes into contact with strong acidic substances such as HC1 aqueous solution after use, which causes pitting corrosion on the surface of 304 ss, destroys the passivation film on its surface, produces crumples, and eventually develops into rust. It is recommended that in the daily work of 304 ss if it comes into contact with strong acid substances, it should be cleaned in time to remove the pollution of corrosive substances.
Fluoride ions exist in salt, seawater, sea breeze, soil, and other environments. ASTM 304 ss corrodes quickly in the presence of fluoride ions, even more than ordinary low carbon steel. If there is a splice on the surface of 304 ss, the corrosion rate of this splice will be greater than that of other parts.
So if the equipment is in a fluoride ion-rich environment, the best way is to replace other materials.
After 304 ss is processed by wire drawing and bending, the surface passivation film and the internal crystal structure of the pipe have been destroyed; if it is not protected by pickling and other protection treatments, it will also be oxidized and rusted.
The above are some of the factors that cause the surface of 304 ss to rust, so you need to pay attention to the following points when using 304 ss:
Keep reading: A Complete Guide to Stainless Steel AISI 4140
For stainless steel, the fusion welding efficiency with and without fillers is excellent. Recommended steel grade 304 filler rods and electrodes are of grade 308. The suggested filler for 304L is 308L. Heavy section-sweated areas can need to be post-welded. This phase for 304L is not necessary. If post-weld heat treatment is not practical, Grade 321 could be in use.
304 ss is a kind of austenitic stainless steel, which has good weldability, but it also has special physical properties, that is, low thermal conductivity, high electrical resistivity and thermal expansion coefficient, and high-strength surface protective film. Due to the characteristics, the welding workpiece will produce large welding deflection deformation, overheating in the near-joint zone, and there are dangers such as thermal cracks, liquefaction cracks, lattice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking. Besides, it also contains a large number of elements with a strong affinity for oxygen. Therefore, the welding process must be reasonably designed according to the physical properties, welding characteristics, and actual working environment of 304 ss to ensure the service life of the welded joint.
Try for free information about the A Complete Guide to Stainless Steel AISI 420
In the welding process of 304 ss, there are often problems of post-weld cooling deformation, such as transverse shrinkage, longitudinal shrinkage, bending, and angular deformation, which will seriously affect the welding quality. To prevent severe deformation of 304 ss structural parts during welding, and to ensure its performance in high-temperature environments, the scientific selection of welding process and welding materials should be combined with the structural characteristics, performance characteristics, and functional requirements of stainless steel components before welding to ensure that the welding process used can meet the performance characteristics of stainless steel components to the greatest extent, to control welding deformation problems.
Compared with SMAW welding, the TIG welding method with the characteristics of low heat input and excellent welding quality is adopted. This method is particularly suitable for welding 304 ss plates, 304 ss coils, and 304 ss pipes. The selection of welding materials for austenitic heat-resistant steel must first ensure the tightness of the weld and the absence of defects such as cracks and pores. At the same time, the thermal strength of the weld metal should be as strong as the base metal. This requires the choice of 304 ss. Welding wire of similar chemical composition. The recommended welding wire is ER308 with a diameter of 2.0 mm.
304 ss has greater heat sensitivity. When welding, the heat input of the joint must be controlled. To prevent the phenomenon of “depleted chromium” in the welded joints and reduce the sensitization temperature range of the joints, the welding heat input should be controlled in a low range. At the same time, to improve the crack resistance of the welded joint in a high-temperature environment, a short arc should be used in the welding process and the arc should be stable during implementation without swinging.
Read more about A Complete Guide to SUS Stainless Steel Banding
Wire diameter/mm
Argon flow/m3h-1
Tungsten electrode diameter/mm
Welding current/A
Welding speed/(mm/s)
2
0.5
2
120-150
3-5
Before welding, use surface treatment technology to polish the metal around the weld to remove the existing oxide film. In addition, clean both sides of the weld with acetone to ensure that there are no oxides, sulfides, etc. during the welding process, so as not to reduce the plasticity, toughness, and fatigue strength of the weld metal and increase the low-temperature brittleness of the inclusions.
In addition to reducing the input current as much as possible, the joint design should be improved to reduce the degree of restraint or restraint strain; the position of welds and grooves should be reasonably arranged, and the direction of shrinkage stress of the weld should be changed; the size of the weld angle should be reduced to reduce stress. Post-weld heat treatment of the welded parts: heat the welded parts to 570°C at a heating rate of 55-200°C/h for 6 h; then cool down at the same rate, and remove the welded parts when the temperature reaches below 400°C Air cooling.
Get it now:A Complete Guide to SUS Stainless Steel Banding
Since in the annealed state, it is non-magnetic and becomes slightly magnetic with the application of cold work. Type 304L stainless steel is commonly in use in welding to prevent the development of chromium carbides during cooling in the weld’s heat-affecting area.
Also, they have less carbide precipitation and localized corrosion, the low carbon version, 304L sheets, are ideal for welding applications.
316/316L stainless steel plates and sheets have a higher nickel content material than ASTM 304 and 304L stainless steel sheets, giving them even better corrosion resistance, especially in marine applications.
There are two types of carbon content material: low carbon and high carbon content material.
As a result, the price of ASTM 304 stainless steel sheets is lower when compared to other stainless steel grades and all metallic items in general.
For completely different variations of the fabric, the sheets and UNS S30400 Stainless Steel Strip Specification vary, as do the applications. Both grades of stainless steel are austenitic, which is one of the most widely used and durable types of steel.
Keep reading:A complete guide to SUS 304 stainless steel
AISI 304 material is just a guideline/reference and does not include physical properties with minimum or maximum values. SS304 applies to various ASTM, BS, etc. standards depending on the nature of the material being tests, for example, SS304 plates meet a different physical ASTM standard while the SS 304 plates will be checked by a different ASTM standard with different physical values. The ASTM standards would be different. The chemical compounds are identical.
Thus, AISI 304 material stands for 304 stainless steel. It doesn’t specify precisely what country norm to take into account, but it doesn’t matter, because most standards are aligned.
AISI 304 material applies primarily to the original US standard defining 304.
AISI 304 material Requests
The most common and used form of stainless steel is the SAE/ANSI 304 or AISI 304 material. Often known as 18/8 stainless steel, A2 stainless steel, or 304S15 according to British Standard (as per ISO 3506). It’s an austenitic chromium-nickel alloy, meaning that it has extremely high corrosion resistance. It is also non-magnetic and cannot be hardened by heating.
Try for free information about the Aisi 304 stainless steel : the best you can find & purchase – Yaoyi
The outdoor cabinetrymaterial for all coastal areas is the preferred marine quality stainless steel. However 304 works just fine in other areas, including the desert, mountains, a city roof, or just your house.
The truth is, most appliance and grill manufacturers use steel grade 304 – in coastal areas too, which requires you to regularly clean and maintain your appliances or keep them covered.
Also, stainless steel does not prove to be stain-free. It is less stain-free. If you are using stainless steel exposed to 304 or 316L, maintenance is of requirement. Adding molybdenum (in marine stainless steel) just delays and does not hinder corrosion.
Steel grade 304 is in use in domestic and industrial applications including food handling and processing devices, screws, machines, utensils, car headers. For external accents, like water and fire in the architectural field, steel grade 304 is also in use. It is also a popular vaporizer spinning material.
Cup
Flowers, screws, nozzles & bolts
Backs and Sinks
Paneling of architecture
Tube
Production equipment in brewery, food, milk, and pharmaceutical
Hygienic goods and troughs
Read more:difference between Stainless Steel 316 and Stainless Steel 316l
For a purpose, at least 10.5% of the make-up must be chromium if a substance is to be called stainless steel. Nickel, titanium, aluminum, copper, nitrogen, phosphorus, selenium, and molybdenum typically include additional alloys. Molybdenum is the main difference between them. Molybdenum increases corrosion resistance, which is the moniker of “sea grade” stainless steel, in an atmosphere rich with salt air and chloride.
Meanwhile, both have the same nominal content of chromium and nickel, which is also the same corrosion, production, and softness resistance.
The 304H carbon (UNS S30409) content is 0,04-0,10%, which gives the highest temperature resistance.
Whereas, the carbon content of 304L (UNS 30403) is limited to a minimum of 0.03% and prevents sensitization during moderation. Sensitization means chromium carbide formation along with the grain limits if the temperature range is around between approx. 480-820°C and the temperature range of stainless steel.
The chromium carbide formation results in lower resistance to corrosion along the grainline and leaves the stainless steel sensitive to unexpected corrosion in an atmosphere in which 304 is in anticipation to be resistant to corrosion. This corrosive grain boundary attack is referred to as intergranular corrosion.
Likewise, the carbon content of 304 (UNS 30400) is up to a maximum of 0.08%. 304L is therefore not helpful in corrosive applications where welding is needed, including corrosive tanks and tubes.
Also, its lack of minimum CO2 is not perfect for applications at high temperatures where optimum strength is in the requirement, 304H is therefore preferable. Therefore, 304 is usually in the limit to bars in machines in components where no welding is necessary or small sheets shaped in articles such as sinks for kitchens or cookware, which are not also under welding.
Carbon content has a significant effect on the strength of the room temperature and the minimum tensile characteristics defined at 304L are therefore less than 5 kilopounds per square inch (34 MPa) for 304.
Nitrogen, therefore, has a powerful role to play with room temperature strength, and 304L of the same tensile strength is made by a small addition of nitrogen. So, almost all 304L are manufactured as dual 304/304L certified, which means that they meet the minimum 304L carbon content and also the minimum 304L tensile strength.
AISI 316L & AISI 316: Everything You Need To Know – Yaoyi stainless steel
The astm 304 stainless steel food grade steel has passed all of the required tests to be considered suitable for food processing, handling, and use. The most common food-grade stainless steel in the form of 304 is stainless steel. But stainless steel sheets (18/8 and 18/10) are other names or codes used for stainless steel 304 grades.
Since there are many types of food-grade stainless steel, each with its structure and properties. Since it contains 18 percent chromium and 8% nickel, it’s known as “18-8” stainless steel, and it’s the most commonly used stainless steel on the earth.
The commonest grades of stainless steel in food processing and mining are 18/8 and 18/10, all in the series 300 and even in type 304. The first statistic, 18, will show the total of the chromium present and the second will show the nickel quantity.
The 304 rating for stainless steel food grade, therefore, covers stainless steel, which meets the Peoples of China National Standard/Sanitary Standard for GB 9684-88, which has a less than normal lead chroma material.
Application of Stainless Steel in Marine Installations
Grade 304 for food-grade stainless steel means interaction with food-grade and such food safety standards must be complied with. Due to the high quality of chromium in the process of food processing, and chromium in the 304 grade of stainless steel, all kinds of toxic chromium can be dissolved in unskilled steel, and it is very important to minimize various impurities of alloys such as plum and cadmium.
On the other hand, human wellbeing can be in jeopardy as 304 stainless steel food-grade materials migrate faster than heavy metals during use.
For this reason, the production of cookware 304 in stainless steel needs a balance between protection against corrosion and security. The anti-corrosion feature is enhanced with high nickel and chromium content, but the amount of precipitated nickel and chromium increases as a result of raising the safety risk.
As a result, national food quality guidelines, such as Stainless Steel Products (GB9684-2011), have stringent controls on the precipitation of chromium, cadmium, copper, lead, and other heavy metals in cookware.
Adding to these, the increase in manganese content in 304 stainless steel food-grade, which is after a lack in cookware functions such as corrosion and rust resistance, is dangerous. Until the contents of manganese are at a certain amount the material cannot be used as cookware or stainless steel cookware. But such a high content of manganese does not affect good health.
Although the level of manganese does not comply with the national food safety standard, it is explicitly stated that 304 food-grade material of stainless steel should be the main component of the food container that satisfies national requirements.
According to the GB9684 standard, astm 304 stainless steel food grade is stainless steel.
Thus, GB 9684-2011 refers to the stainless steel content grade 304, classified as stainless steel, defined in the National Sanitary Standard for Stainless Steel containers of the People’s Republic of China. This stainless steel alloy is smaller than normal steel.
Furthermore, the protection of the substance in the fight against corrosion has improved; Chromium (Cr), mg/L 4% solution of acetic acid soak 1.0 1.0. (Pb) lead, mg/L 4% acetic acid solution soaking. 1.0 1.0. Acetic acid solution of nickel (in terms of Ni) mg/L 4 percent 0.5. Acetic acid soaking solution of 4 percent (Ni). 0.02 0.02 tin (Sn), 4% acetic acid solution, mg/L 3.01.0. 0.04 0.04 Acetic acid solution (as As), mg/L 4 per cent.
On the other side, the stainless steel 304, which is used for the production of appliances and parts requiring high total durabilities, such as corrosion resistance and formability, is robust stainless steel.
To preserve resistance to corrosion found in food grades 304 of steel, steel must also be produced from over 17% chromium and 8% nickel.
However, we are well aware that in the food industry, stainless steel products should be 304. The food-grade of 304 stainless steel is the most common food-grade stainless steel used in day-to-day needs, which has excellent acid and alkaline resistance and high corrosion resistance.
Moreover, the 304 has a higher chromium content, a matte finish, which does not rust. There is a comparison between the two as they are in pairs together. The difference in corrosion resistance is the most significant factor.
We probably come into contact with stainless steel products in daily life, one of which is electric steel kettles.
The laboratory method is used mainly to detect the structure of the material as these various stainless steel substances are differentiated.
Steel 304 generally refers to stainless steel that satisfies the national demands of the GB9684, which may affect food, regardless of physical harm. GB9864 stainless steel is food-grade stainless steel, as GB9684 is a national quality certified stainless steel.
Moreover, 304 stainless steel is not stainless steel of food quality; it is not only available in kitchen utensils but is also used in production and the threat to the body is not uncertain. The standard commodity on the outer and internal walls of the product shall have a standard commodity of 304 stainless steel grades, and the product rating GB968 on the footnote 304 shall be safer.
Stainless Steel Application of Medical Treatment
The stainless steel grade 304 is a popular choice for the treatment of healthy food grade. Not only does stainless steel with a food grade withstand plastic-melting temperatures, but even its antioxidant coating prevents food contamination from being corrosive.
However, before using it in the manufacturing process, you should know some things about food grade, just as for other items.
stainless steel is famous for its corrosion resistance, but it doesn’t imply food quality simply because the surface appears polished and smooth.
To follow important sanitary requirements, the steel finish must be free of all surfaces that could harbor bacteria while still being easy to clean and sanitize.
Furthermore, electropolishing is preferred to physically grind down surfaces in this case. This is because electropolishing removes the steel’s surface coating, revealing a microscopically smooth substrate.
Even so, it does not only strengthens the oxide layer of stainless steel but also eliminates microscopic defects that could host bacteria.
Metal scrub brushes should not be used in food-grade stainless steel. A common alternative to deep tints on metallic surfaces is steel wire brushes. These brushes cannot be applied in stainless steel scrubbing on the other hand.
However, simple steel particles in the brush may be trapped in the stainless steel crust, thus jeopardizing the quality of the protective oxide sheet. Edelstahl rolls like ordinary steel over time.
You should also avoid using the same materials to wash stainless and non-stainless steel. The stainless steel may be contaminated with plain steel particles.
3: Food-Grade Stainless Steel Alloys Are Not All Created Equal
Only because a steel alloy is in brand 304 stainless steel food grade doesn’t mean it’s appropriate for the manufacturing operation.
As there are several different stainless steel alloys on the market, each has different chemical tolerance and manufacturing conditions benefits and disadvantages.
While Grade 304 is corrosion-resistant, if the stainless steel is exposed to salt, it will corrosive for a long time. Grade 304 in stainless steel is not suitable for any process involving recurrent, long-term salt or saltwater exposure.
Stainless steel types can be contaminated by very low temperatures. The melting point of most stainless steel is far above the temperature levels used in most food processing processes. When choosing food-grade stainless steel (and any possible coatings for it), it’s always important to consider temperature extremes in the manufacturing process.
According to Gasparini Industries, a significant number of stainless steel alloys are caused by true cryogenic conditions below -49oF. In the event of a sudden, rapid change in temperature, the crystalline expansion causes the metals to warp or crack as metals are heated.
Therefore, martensitic stainless steels are suitable for very low temperatures. This is because if the temperatures are mild, the structure of martensitic steel is less susceptible to fragility.
The possibility of oxidation with the use of stainless steel alloy in food quality at high temperatures is also important to note. In such applications, stainless steel 304 grades are mostly used due to their capacity to withstand oxidation up to 1697oF. This is well beyond the limit of almost any food processing technique between applications without sterilization baskets.
In addition to the protective oxide coating that delivers food-grade making stainless steel alloys with their corrosion resistance and unlike filler materials during such welding operations, heat stress can be removed. As a result, improperly welded forms of metal corrode more quickly than they should.
Since the system can finish precisely welds without the use of over-heat or fillers, a resistance welding process with a high precision medium-frequency direct current MFDC machine reduces the risk of changing the protective oxide coating of the welding steel.
STAINLESS STEEL APPLICATION OF STAINLESS STEEL WASHER
Austenitic, duplex and ferritic stainless steels are all included in the specification. Each grade of steel covered by the specification has its chemical composition and tensile properties listed. If you were ordering a 25mm diameter bar, you could specify ASTM A276 and then specify the steel grade. ASTM 304 is a good example.
However, you would not use ASTM A276 if you required cast stainless steel or stainless steel plate.
In the presence of holes, crevice corrosion occurs. ASTM ASTM 304 stainless steel is often mixed with other materials in modern industry, resulting in gaps in the instrument. Crevice corrosion is quick to happen when the void is large enough for an industrial solvent or liquid to join. Aside from gaps in the weld, there has been a case where a solution containing oxygen ions has caused gaps in ASTM ASTM 304 stainless steel.
As a result, to respond to this ASTM ASTM 304 stainless steel inspection, each item must be judged individually based on various corrosion conditions.
Factors causing ASTM 304 stainless steel plate crevice corrosion
Resulting in There are several corrosion factors in ASTM ASTM 304 stainless steel. Corrosion is affected by the gap’s width, length, form, and area. Corrosion begins when the solution reaches the void.
Thus, the rate of corrosion increases as the concentration of oxygen in the reagent rises. The higher the temperature in a closed setting, the faster the corrosion rate. The more chloride ions present, the more likely crevice corrosion is.
Why do you Purchase the Stainless Steel Flat from Yaoyi ?
An attempt to resolve operational issues and reduce the number of equipment holes. There is no residual solution in the equipment after the test or manufacturing phase is in creation. When it comes to ASTM A240 ASTM 304 stainless steel, it’s important to know how to spot fakes and shoddy goods.
Accordingly, standard manufacturers can sell ASTM A240 ASTM 304 stainless steel. Stainless steel with good corrosion resistance is usually costly and must be carefully put into consideration.
Study Stainless Steel Technical Made Simple: A Step-by-Step Guide
There is commercially available flatware is ASTM 304 stainless steel or also known as 18/10 in the kitchen merchandising industry, which stands for 18 percent chromium + 10% nickel. 316 is almost the same, but with a little more molybdenum added to boost corrosion resistance even more. Because it is a little more expensive and especially corrosion-resistant. ASTM 304 is more commonly used in the serious lab, pharma manufacturing, and prosthetic/medical implant applications.
ASTM 304 is perfectly adequate for most kitchenapplications, which is why it is so common.
FOCUSED ON THE 0.03 ~ 0.05 mm Stainless Steel Foil
With this in mind, it is non-magnetic and electrically, and thermally conductive. It has outstanding shaping abilities and is commonly in use as a result of this. Grade ASTM 304 is resistant to a wide variety of corrosive media, both ambient and otherwise. Type ASTM 304 can be in use in a wide range of household and industrial applications. It’s also in use in the architectural sector for exterior features like water and fire.
Get it now:AISIComparison of Stainless Steel Standards in Different Countries
AISI is a famous abbreviation that stands for American Iron and Steel Institute. Founded back in 1908, AISI is known for successfully standardizing the numbering system for steel we have today with the collaboration of the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE)
The Society of Engineers is a global association of engineers specializing in aerospace, vehicles, and automotive.
The Guide Of American Stainless Steel Tube Standard
AISI 304 stainless steel is a form of chromium-nickel stainless steel that is capable of many things as it is versatile, easy to form, has strong resistance, and many more! This is the reason why the AISI 304 stainless steel is commonly found in constructions and as well as common household items.
More examples of which will be given further in the article. But first, let us look into the different categories of stainless steel to get a better understanding of its characteristics.
Below are the three main categories of stainless steel. Each of which is unique from one another and it has functions that only it can do in its field as well. It is appropriate to start with austenitic steel first since the AISI 304 stainless steel is part of that category.
How do you care of stainless steel?
Austenitic stainless steel is one of the most used types of stainless steel due to its high chromium content that is far from other steel alloys. The high chromium content provides a higher resistance to corrosion.
However, this type of steel tends to be non-magnetic, but when cold work is applied, it may have magnetics capabilities afterward. The AISI 304 stainless steel belongs to the austenitic stainless steel category.
Other Austenitic stainless steel examples:
How to Remove The Oxide Scale on The Surface of Stainless Steel Casting Billet?
Martensitic stainless steel is the least common in the category, this is because it has the lowest resistance among the three classifications of steel. But when it comes to hardness, it has absolutely high hardenability.
Its strength and impact resistance are extraordinary which makes them ideal for applications that require durability.
Examples of Martensitic Stainless Steel
What are the Pros and Cons of Stainlesss Steel Wire?
Ferritic stainless steel is second for being the most used stainless steel in the industry. They are known for their magnetic properties and these alloys can be hardened through the process of cold working.
Ferritic stainless steel tends to be less expensive as well when it comes to price because of their low nickel content.
Example of Ferritic Stainless Steel
Why Choose Yaoyi to do the Stainless Steel Edging?
The AISI 304 stainless steel has several thermal properties. Below are the commonly searched thermal categories.
Heat capacity refers to how many heat units a steel can intake. For the AISI 304 stainless steel, it is capable of withstanding 0.5 J/g-°C
When it comes to thermal conductivity, the AISI 304 stainless steel has a rate of 16.2 W/m-K.
For the melting point, the AISI 304 stainless steel can withstand a temperature of 1400 – 1455 °C before showing signs of melting.
Get it now:AISI 302 Stainless Steel
Physical properties are different from mechanical properties. So, do not confuse these two separate categories with one another. In terms of the physical properties of the AISI 304 stainless steel, we will only be discussing one:
The AISI 304 stainless steel has a density rate of 8 g/cc. Density is crucial for a stainless steel’s tone and performance.
In this section, you will learn why the AISI 304 stainless steel is strong. For comparison of other stainless steels’ mechanical properties you may check YAOYI’s mechanical properties table.
Tensile strength refers to the tension resistance being pulled apart. In much simpler terms, it is the resistance of a certain material to breaking under tension. The tensile strength of the AISI 304 stainless steel is 73,200 psi.
Yield strength is the capacity of a steel to go under stress before showing signs of deformation, cracks, or damages. The yield strength of the AISI 304 stainless steel is 31,200 psi
Elongation is the measurement of how much a steel can stretch from its original length and it is measured in percentage. The elongation rate of the AISI 304 stainless steel is 70%
Modulus of elasticity is somewhat similar to elongation but it does not measure how much the steel can stretch, rather, it measures the rate of the steel’s tensile stress to tensile strain. The AISI 304 stainless steel has a modulus of elasticity of 28,000 – 29,000 ksi.
Charpy impact or charpy test is the indicator measurement of a material if it is ductile or brittle. In this case, the AISI 304 stainless steel is a ductile material with a measurement or rate of 240 ft-lb.
This refers to the hardenability of the steel in a Rockwell B scale. The AISI 304 stainless steel has a hardness rate of 70.
How to Buy Stainless Steel Coil Springs Raw Material?
In this section, you will learn why the AISI 304 stainless steel has superior corrosion resistance. You can compare other stainless steel’s chemical composition in YAOYI’s chemical composition of stainless steel chart
AISI 304 is primarily composed of 7.5-19.5% Chromium and 8-10.5% Nickel. This amount is responsible for its outstanding corrosion resistance.
Below are its other elements.
4 Common Methods for Welding Stainless Steel Pipe
In case you are still wondering what are the other projects that AISI 304 stainless steel can be used for. Below are its common uses.
There are tons of stainless steel sinks out there that use AISI 304 as its material, this is because of AISI 304 stainless steel’s corrosion-resistant property, which makes the sink’s longevity extend much more than the average steel sink.
Cheap Cooking pans with low steel grades tend to get rusty in the long run, which is both unsafe and impermanent. With AISI 304 stainless steel cooking pans, you’ll not have to worry about any of those concerns.
Tubes are very prone to corrosion, and just because of that main reason, industries prefer to use AISI 304’s since they cannot be threatened with corrosion damages.
AISI 304 stainless steel can be commonly found in dryers. refrigerators, water heaters, kitchenware, washers, and many more. But that does not necessarily mean that these appliances in your home are automatically AISI 304s.
Some appliances use low-grade steels which are the cheap ones.
This prevents the food from contaminating, and it also maintains the freshness of the food items. However, the common grade steel usually used in food processing is not 304s but rather 316s which is also known as “ Food Grade Stainless”.
AISI 304 stainless steel is great for heat exchangers as they can withstand extremely hot temperatures without damage whatsoever. Stainless steel is also common in heat exchangers, regardless of its steel grade.
When it comes to heat exchangers, 316LL SS is more corrosion-resistant than its lower grades.
There is without a doubt that AISI 304 stainless steel is mostly present in structures for various reasons but mainly because of their corrosion-resistant properties and formability. It is highly recommended that for structures,
If you need AISI 304 stainless steel or other stainless steel products for your project structures, our services will get on to processing immediately, shortly after a discussion of what you specifically require.
Always Provides You with the BEST Austenitic Stainless Steel Products
Yes, it may be corrosion-resistant but when it comes to rust, it accumulates at a fast pace in hot humid climates.
Yes, it holds its reputation very well and is widely used by people, businesses, and industries until this day. It’s durable, it extends longevity, affordable, and versatile. This is one of the reasons why it can be applied to home appliances and commercial food processing.
Everything You Need To Know:Stainless Steel Ties
There’s this term called “ Food Grade Stainless Steel “ which refers to steel that met all the safety standards for it to be approved for storage, preparation, and serving. For AISI 304 stainless steel, it is safe and 304 is considered to be the most common grade steel for food grade.
Your Best Supplier Of Stainless Steel Coil Always Provide You With SS Coil From China
For those who want extra security, AISI 304 stainless steel is officially FDA approved. Its mechanical properties are above the FDA minimum which is considered to be safe to use.
This is the reason why back in the early days, the demand for 304 was high because of food marketing experts demanding 304 kitchenware for their advertising.
Stainless Steel AISI 316Ti (S31635) By The AISI System
AISI 304 is indeed magnetic, and as well as 316. Both stainless steels hold paramagnetic characteristics. So, don’t be surprised if a magnet sticks to them because these properties can even be attracted to magnetic separators.
J2 Stainless Steel: A Complete & Thorough Guide
There are more than 100 types of different steels in the market but what’s commonly being compared to 304 stainless steel is 316 stainless steel. This is because both types of steel have an equally high demand and there are more similarities between them compared to their differences.
However, it can be very hard to tell the difference between them with just the naked eye, which is the case for the 304 stainless steel and 316 stainless steel.
For Mechanical Properties, the 304 stainless steel contains 18% Chromium and 8% Nickel while 316s contains 16% Chromium, 10% Nickel, and 2% Molybdenum which the 304 does not have.
But when it comes to formability, AISI 304 stainless steel is better than 316 because Molybdenum prevents it from flexing as far as 304’s go.
AISI 304 2B: One Of The Most Commonly Used Stainless Steel
Like any other stainless steel product, each type of steel has its advantages and disadvantages. It has its purposes as well that only fits for a certain project.
AISI 304 Stainless steel is way easier to clean compared to other steel grades. A dampened microfiber cloth to wipe 304 stainless steel is already effective.
With high tensile strength and strong mechanical properties, its durability plays a vital role in its longevity. Making it highly resistant to its opposing elements. Even if it’s strong, they are extremely flexible.
AISI 304 stainless steel is known to be superb when it comes to corrosion resistance, which is one of the main reasons why manufacturers use this product for common household items because it is safe, and even FDA approved.
One thing we have not yet mentioned is that AISI 304 is also oxidation-resistant. Meaning, it is also resistant to intergranular corrosion such as acids with a concentration percentage below 65% .
AISI 304 can withstand both hot and cold forming processes and performance which is a huge advantage. This is because 304s are engineered to be adaptable when it comes to formability.
Without a doubt, AISI 304 stainless steels are versatile. Different manufacturers choose 304s because they can be turned into almost anything without having little to no issues in terms of formability.
When temperatures reach -180 ℃, AISI 304 stainless steel becomes stronger with a great elongation and area reduction rate. This means to say that there would be no issues using 304s in temperatures -180 ℃.
AISI 304 stainless steels are known to have difficult machining characteristics due to their rapid hardening rate.
In Chloride environments, AISI 304 Stainless steel is susceptible to pitting and crevice corrosion which is something to consider if you are planning to place it in chloride environments. This generates “ pitting “which is small areas of localized corrosion.
Despite the versatility of AISI 304 stainless steels, one of the big disadvantages of them is that they do not do well in saline environments like areas near a coastline. This is associated with the weakness above which is the involvement of chloride.
AISI 304 2B: One Of The Most Commonly Used Stainless Steel
Absolutely, density can also be measured in lb/in3 (pounds per cubic inch). The density of stainless steel is about 0.289 lb/in3. This is another way to express the same property we discussed earlier.
Yes, the density of AISI 304 Stainless Steel, which is around 8.0 g/cm3 or 0.289 lb/in3, affects its applications. This property is important in many situations where weight and volume considerations come into play. For example, in the construction industry, knowing the density is vital when considering the load-bearing capabilities of a structure. In the transport sector, a lower density might be preferable to keep the weight down for fuel efficiency.
Keep in mind that these figures are typical and may vary slightly depending on the specific piece of steel and the manufacturing process used. Always refer to the manufacturer’s data for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
The yield strength of 304 stainless steel, at 205 MPa, makes it a suitable material for many structural applications. It can sustain significant stress before it begins to deform permanently, which is a crucial property in structures that need to support large loads. However, it’s always important to consider the specific requirements of each application, as other materials may be more suitable based on factors like corrosion resistance, temperature resistance, and cost.
Remember, these descriptions provide a general understanding of AISI 304 Stainless Steel properties. For detailed specifications or particular applications, it’s always best to consult with a material scientist or a trusted steel supplier.